XPress: Simple Truth Expression Language
Background
How many times you needed a quick, simple method to create expressions in a Json or XML element value. and you wished there were an easy wy to create dynamic expressions at compile time as a literal string to be compiled and evaluated at runtime using the same powerful CLR. Well, I have!
The need for string expressions that can be simply expressed at compile time by engineers or non-engineering business or support team, has been a recurring theme through out my career. Whether its is business rules, business teams needs to modify it and change it frequently at runtime. or operation rules that devops team would like to control at runtime without the need to make a new deployment.
Goals
So, I rolled up my sleeves and created XPress. It came handy in many situations and i used it in different product and solution. I had a few goals in mind when I designed XPress:
- Simple, yet powerful.
- Contained as possible, as little dependencies as possible.
- few to zero configurations.
- Purely written in C# and .net.
- Fast, and efficient.
- Generates an optimized cacheable .net expressions .
- Support all truth operators (
Binary,Unary,Relational, andConditional). - Support basic data types
int32,string,boolean,float. - Support variable binding at runtime.
- Ability to check on
null-ability.
How it works?
PM> Install-Package XPressXPress is simple, all you have to do after installing XPress package using nuget manager, is instantiating XpressCompiler, author XPress expressions, compile it, and execute it. here is a simple XPress sample code:
XpressCompiler _compiler = XpressCompiler.Default;
// Create and Compile Expression
var expression = "x gt y*2";
var compilationResult = _compiler.Compile(code);
// Create XpressRuntimeContext object with variable names and values
XpressRuntimeContext runtimeCtx = new XpressRuntimeContext() { { "x", "10" }, { "y", "9" } };
// Call compiled Func with runtime context
var result = compilationResult.Code(runtimeCtx);As you can see, XPress language doesn’t need much. very little configuration to start and you’re good to go. If you notice I used XpressCompiler.Default a singleton compiler instance can be used quickly to compile expressions. But a compiler instance can be always instantiated through constructor.
XpressCompiler _compiler = new XpressCompiler();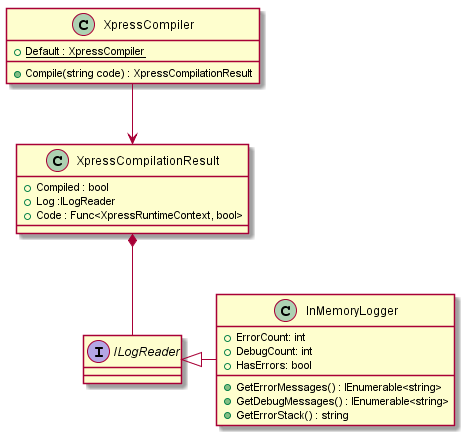
The compiler class offers a single method Compile(string) taking an xpress expression and return a compilation result. The XpressCompilationResult object offers a boolean flag Compiled to indicate the success or failure of the compilation process, and a Log object of type ILogReader which can be used to get status on compilation process and debug the result. a particularly useful pattern after compilation process is to check the HasErrors fla, if true GetErrorMessages() and print it or log it.
if (compilationResult.Log.HasErrors)
{
var errors = compilationResult.Log.GetErrorMessages();
foreach(var error in errors)
{
Console.WriteLine(error);
}
}Finally, the compilation result object, will have a Code predicate of type Func<XpressRuntimeContext, bool> that is the optimized compiled .net expression tree for your string expression. it accepts XpressRuntimeContext which is simply a strongly typed dictionary of <string,string> to bind expression’s variables to runtime values. use the XpressRuntimeContext object to pass values to your variables. Code predicate jsut like any other .net Func can be cached and executed multiple time. the result of execution is a boolean.
Language Features
Variables
Variables literals can be used anywhere within an expression
The variable name follows same C# variable literals naming constraints. It Must start with a letter, or _, and it may contain Unicode letter characters, decimal digit characters, Unicode connecting characters, Unicode combining characters, or Unicode formatting characters.
var e = "y eq x+2*2-4/2";Operands
XPress supports boolean literals of true and false values, numerical operands of int32 and float decimal values, and string operands. notice how the operand values are defined in the next sample code:
var e1 = "true";
var e2 = "false";
var e3 = "9 gt 10";
var e4 = " 'Ahmed' eq 'ahmed'";a null operands can also be expressed to compare a string with nothing
var e = " 'Ahmed' ne null";Binary Expressions
+, -, *, /, % is supported on numerical operands
var e = "x eq (1+2)";If + or - operators applied to a string operands it will act as String.concat()
var e = "x eq ('ahmed '+'elmalt')";Note: Binary operators can’t be applied to mixed types of operands.
Unary Expressions
At the moment only unary logical operators are supported. not can onyl be applied to boolean operands or expressions.
// boolean operands
var e1 = "not false";
// boolean variables, the value of x must be set to a boolean value at runtime or runtime error
var e2 = "not x";
// boolean expression
var e3 = "not ('a' eq 'b' and 9 gt 10)";Notice i applied not to variable x in the previous example. which is acceptable by XPress compiler. it will assume that value of x will be boolean at runtime otherwise it will throw a runtime exception.
Relational Expressions
The following relational expressions are supported:
eqEqualneNot EqualgtGreater ThanltLess ThangeGreater Than or EqualleLess Than or Equal
var e = "1 eq 4";Conditional Expressions
The real power of XPress is composition, you can compose powerful expressions using conditional logical and and or
orLogical ORandLogical AND
var e = "false or x lt 2";Operator Precedence
- Parentheses:
() - Unary Logial Operators:
not - Binary Multiplicative Operators:
*,/,% - Binary Additive Operators:
+,- - Equality Operators:
eq,ne - Logical Operators:
gt,lt,ge,le -
Conditional Operators:
and,or XPressis very powerful and can be used to compose sophisticated boolean expressions as strings.
var e = "(x ne null and x+1 gt 10) or (y ne null and (y*(5+1)-2) lt 5)";What about performance?
XPress is built to be fast and optimized to generated very efficient .net lambda expressions. the most expensive part of the process as you can expect is the compilation of expressions, but this phase needs to occur once, and the result can be cached for the lifetime of the application. on average Xpress compilation phase takes about ~120ms.
Find more information about XPress on project github repository. I will be blogging more in the future about the internals implementation of the language and its compiler.
XPress is distributed under MIT license. What are you waiting, give it a try and let me know what you think!
Happy Coding!





Leave a Comment